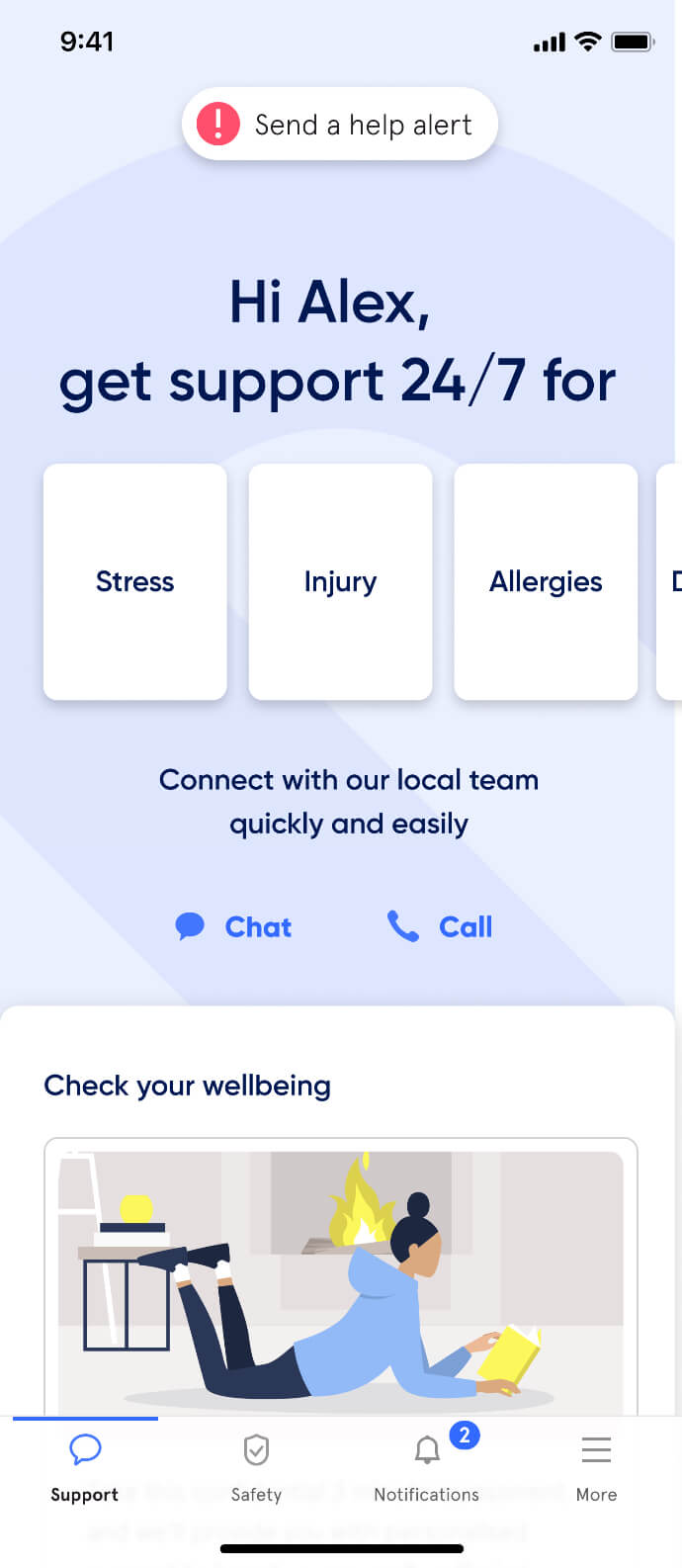
Active Care - your way
When you’re in control, empowered and involved, you’re 80% more likely to have a better outcome.
(Source: Sonder member feedback)
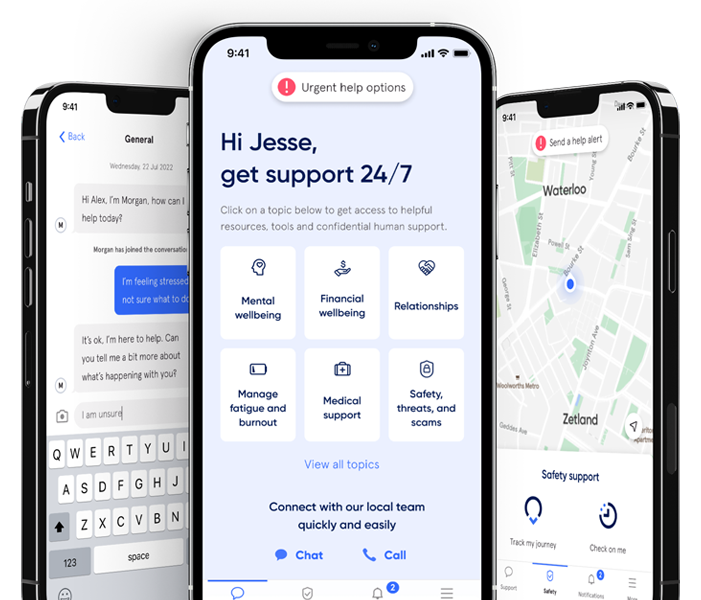
Help in one place.
From burns... to burnout.
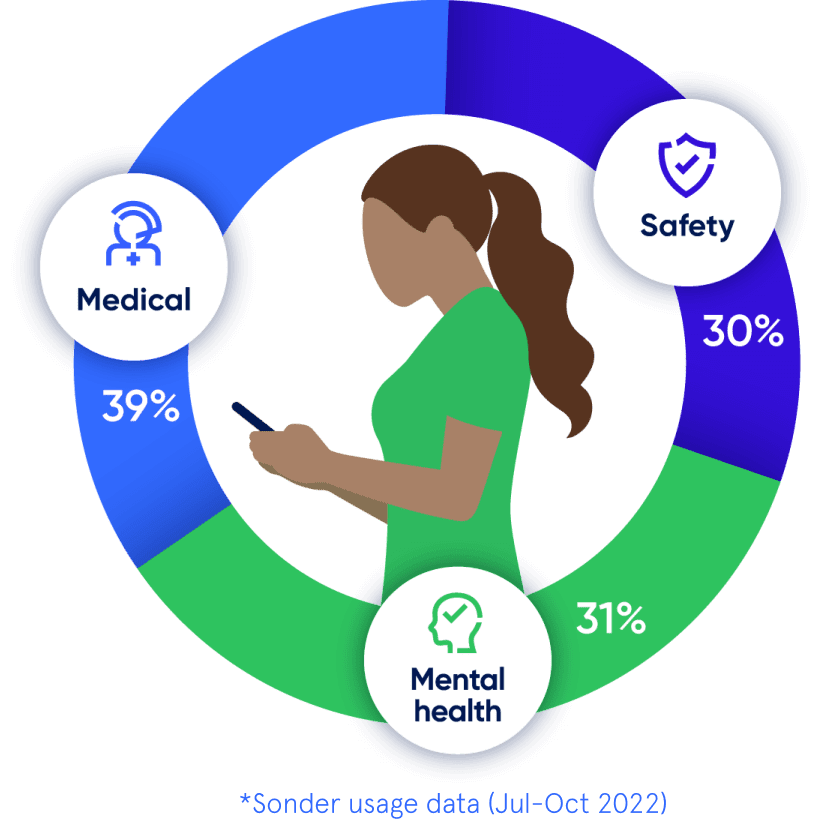
Medical, safety, and mental health are all connected. With 72% of Sonder cases including 2+ underlying issues*, we believe in treating the person first, not the symptoms. Sonder's certified model and accredited professionals provide world-class care for your people.
Accreditations
Australia

Australia

New Zealand

New Zealand

United Kingdom
More care, more often
Support provided after hours
57%
Use live chat
94%
Complex cases which include 2+ underlying issues
(mental health, safety, medical)
Complex cases which include 2+ underlying issues (mental health, safety, medical)
72%
Wouldn’t have reached out without Sonder
55%
Organisational impact
Uptake vs EAP
Saved management time
Employees reported a rise in confidence
Cost saving vs EAP
(35% average uptake)
“No disrespect to our prior EAP providers, but they aren't in the 21st century.”
Kate Mayers, WHS Manager - People & Culture | Best & Less
The complete employee care platform
Support made simple. We make it easy for your people to get the wellbeing and safety support they need, when and how they need it.
The complete employee care platform
Support made simple. We make it easy for your people to get the wellbeing and safety support they need, when and how they need it.
Customers choosing Active Care
- All
- All
- Government
- Education
- Social services
- Corporate
- Customer stories
























Latest insights
Evidence-based reports, insights, and guides for empowering health and wellbeing.
How Sonder provides support to frontline workers facing customer hostility
Discover how businesses like Universal Store and TFE Hotels are using Sonder’s digital services and responsive human support to keep their employees safe and prevent harm.
New report: 75% of frontline workers experience customer aggression
Customer aggression is on the rise in Australia and New Zealand – with more frontline workers being affected, more frequently. Our new report deep dives into the survey data and shares strategies to reduce the risk and keep staff safe.
Kontor provides employees with complete wellbeing support through Sonder
With an expanding team to care for, Kontor needed a simple solution to support their staff. In December 2023, they partnered with Sonder to provide mental health, safety and medical support, all in one place. Whether it’s a billion…
How TFE Hotels revolutionised lone worker safety
TFE Hotels’ preventative approach to their employee risk challenge has not only improved lone worker safety but also built familiarity and trust with Sonder. This has led to an uptake of other health and wellbeing services available via the app, such as 24/7 medical advice for TFE employees and their families.
Put care in the hands of your people
Find out how we can help make a meaningful difference for your people and your organisation.